Globally certified. Locally accessible.
Incident Commander & Crisis Management Team (ICCMT) Development Program
Equip your Incident Commander and Crisis Management Team with the expertise to manage a crisis that can affect the whole community. HRD Corp claimable.
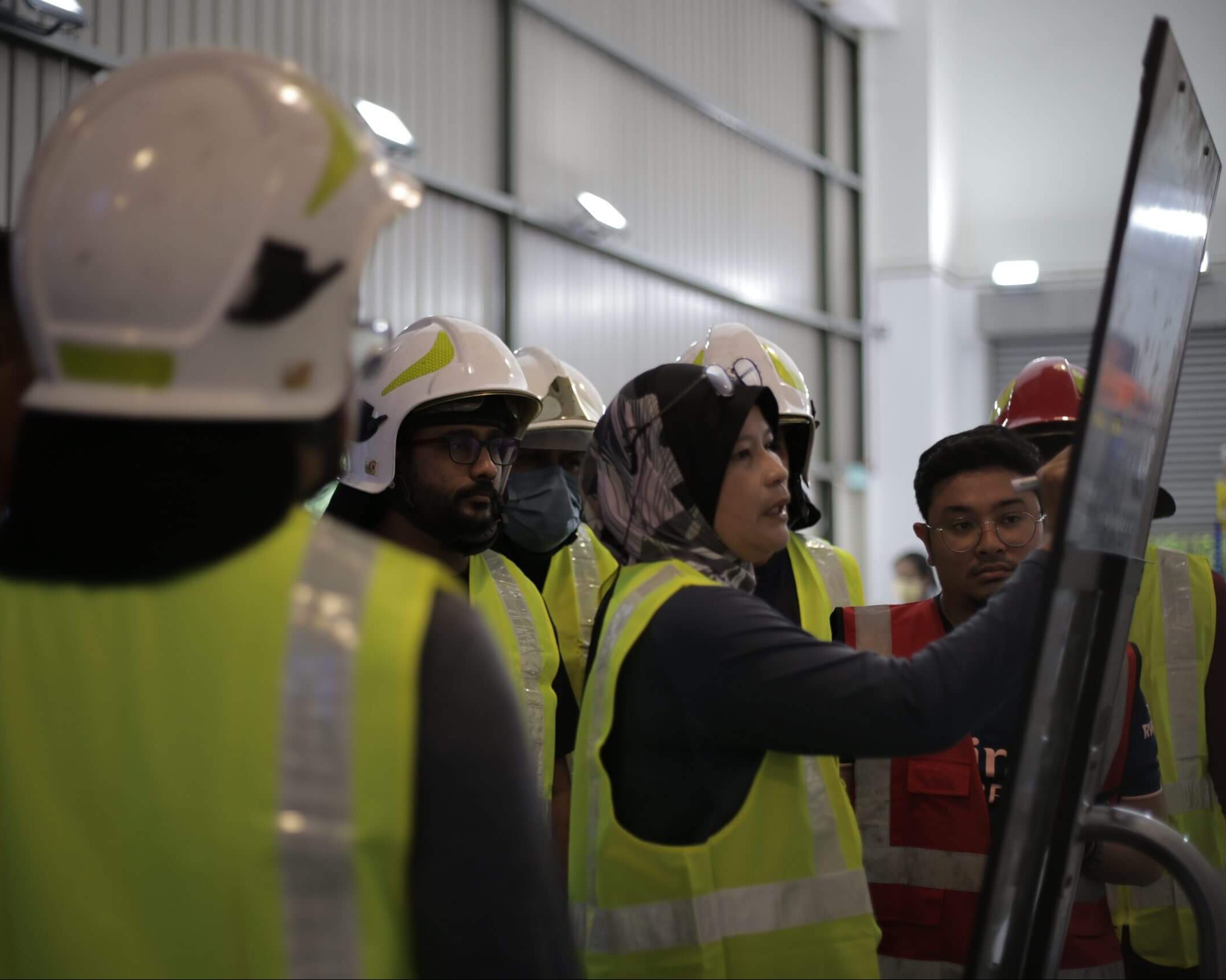

Completing the course, participants will be able to:
Adaptability and Crisis Response
This program focuses on training participants to catch up with unknown and surprising developments that often occur during crisis situations. Through practical scenarios and simulations, participants will learn how to respond swiftly and effectively to rapidly changing circumstances,
ensuring they remain in control during the most critical moments.Incident Management and Coordination
The program delves deep into the five key management functions of Incident Command System (ICS) – Command, Planning, Logistics, Operations, and Administration. Not only will participants learn about their specific roles and responsibilities within each function, but they will also gain a thorough understanding of how these functions coordinate and work together within the Emergency Operations Center (EOC).
- Multi-Agency Command Experience
As part of the program, participants will be exposed
to an introduction to ICS 300 drill, which involves multi-agency command. This experience will enable them to handle large-scale incidents that require collaboration and coordination with multiple agencies and stakeholders effectively. - LIPS Principle Guided Decision Making
In times of chaos, quick and informed decision-making is essential. We integrate the FEMA renowned “LIPS” Principle Guided Decision Making approach, empowering participants to make sound decisions based on the four key factors: Legal, Insurance, Political, and Safety. This principle
provides a structured framework for making critical
decisions under pressure. - Liaison and Financial Administration
To effectively manage a crisis, it is essential to consider various external factors, including interactions with family members, media, social media, authorities, political influencers, and stakeholders. Our program includes an introduction to liaison strategies and financial administration during times of crisis, ensuring participants are well-prepared to handle the complexities of real-world crisis situations.
Completing the course, participants will be able to:
- Enhanced Crisis Management Framework
Level 2 of the program introduces participants to an
advanced crisis management framework that provides structure and organization during times of chaos. By implementing this framework, organizations can respond to crises in a more systematic and effective manner, mitigating risks and minimizing potential damage. - Handling Expanding Incidents
Crisis incidents can rapidly escalate, extending beyond the usual scope of ERT Command and Control. Participants will learn how to adapt to these expanding incidents, ensuring that they remain in control and effectively manage the evolving challenges.
- Integration of Business Continuity Management
Crisis management and business continuity are closely interconnected. Our training program bridges the gap between crisis management and business continuity, enabling participants to understand and implement strategies that ensure minimum damage and smooth transition from Crisis Management to Business Continuity Operation.
- Operational Period Management
Crisis situations can extend beyond a single shift or a standard workday. Our program introduces the concept of “Operational Period” management, which equips participants to handle crises that last for extended periods, ranging from hours to days, weeks, or even months. This approach ensures sustained and efficient crisis response and management.
- ASEC’s Unique Methodology – Parallel Emergency
Operation Center (EOC)Our training showcases ASEC’s unique approach of establishing a “Parallel Emergency Operation Center (EOC).” This strategy emphasizes coordination between the organization’s EOC and the Authority EOC. By working in parallel with the Authority EOC, organizations can proactively anticipate crisis impacts, preempt
announcements, authorize the next course of action,
and effectively manage responses by affected parties and communities. This approach is instrumental in safeguarding the company’s reputation, ensuring business continuity, and minimizing the overall impact of the crisis.
Trainings designed by ASEC trainers certified in

Incident Command System by the Emergency Management Institute, FEMA, US

Master’s of Emergency Response & Planning at Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM)
National Board on Fire Service Professional Qualifications (Pro Board)
ASEC is designated as

TOP 20 HRDF Training Provider with 5 stars excellence in delivery in 2017
ICCMT Development Program can make a difference Beyond your workplace
Navigate through the crisis phase of an incident and seamlessly transition into the incident management phase.
Motivating & Inspiring
Confidence is crucial in acting fast with the right approach in face of an emergency.

Engaging & Realistic
Actionable skills are taught through theories, practical, and mock drills.
Professional Trainers
ASEC’s trainers are qualified and continuously improved to deliver effective training.
Comprehensive coverage
The public and surrounding communities are taken into account.
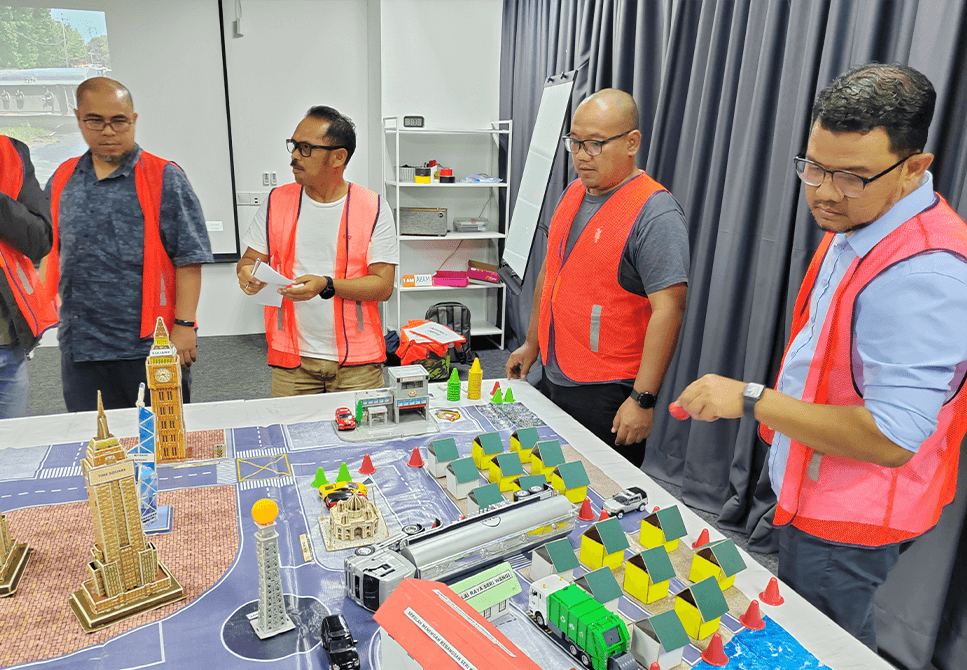
ICCMT Development Program conducted at ASEC
For organizations that value the employees’ preparedness in facing possible crisis involving the public and surrounding communities.
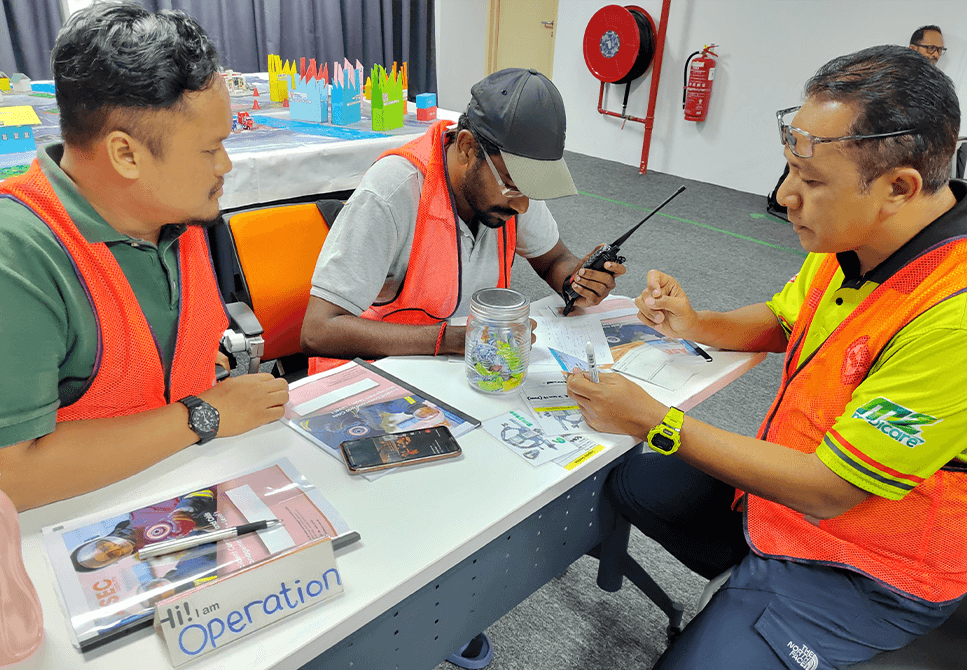
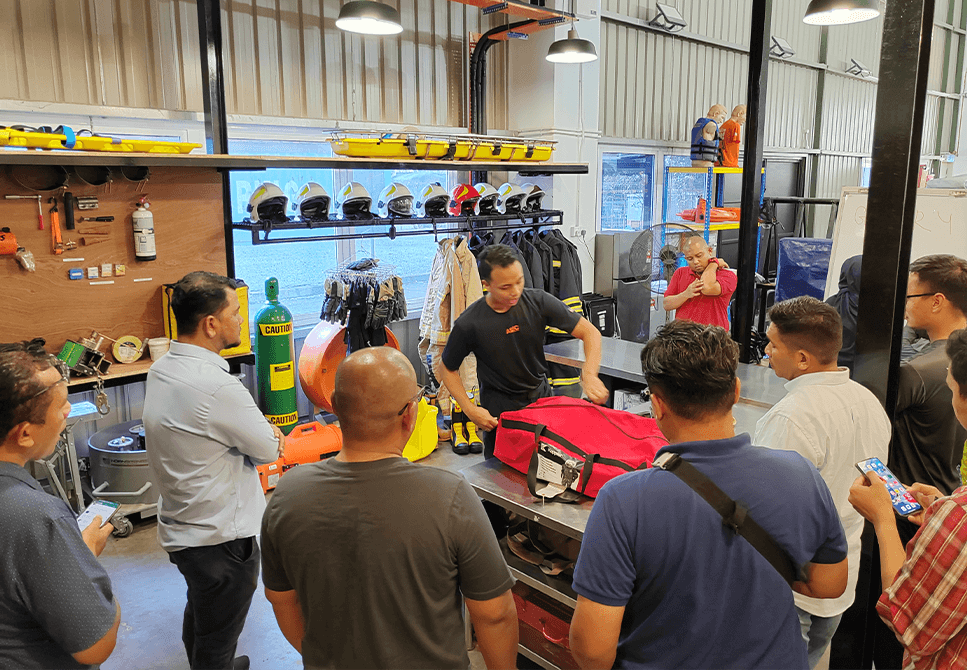
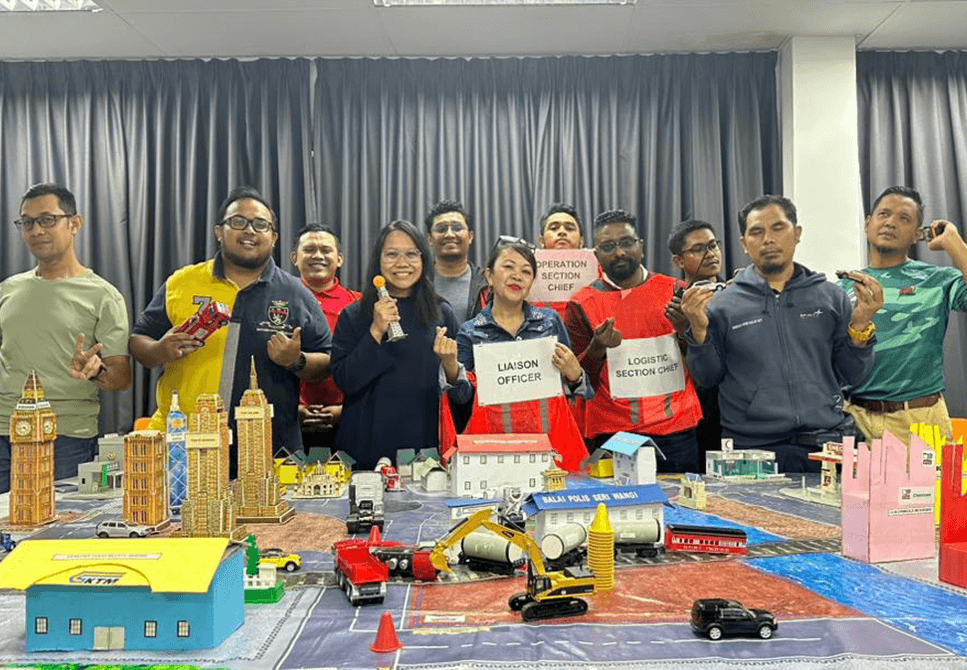
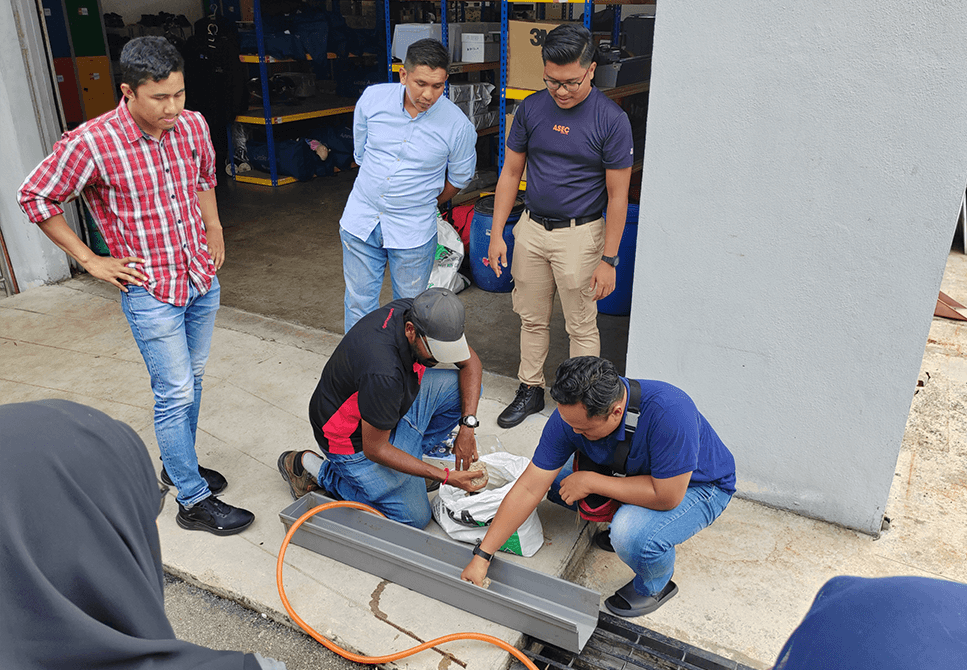
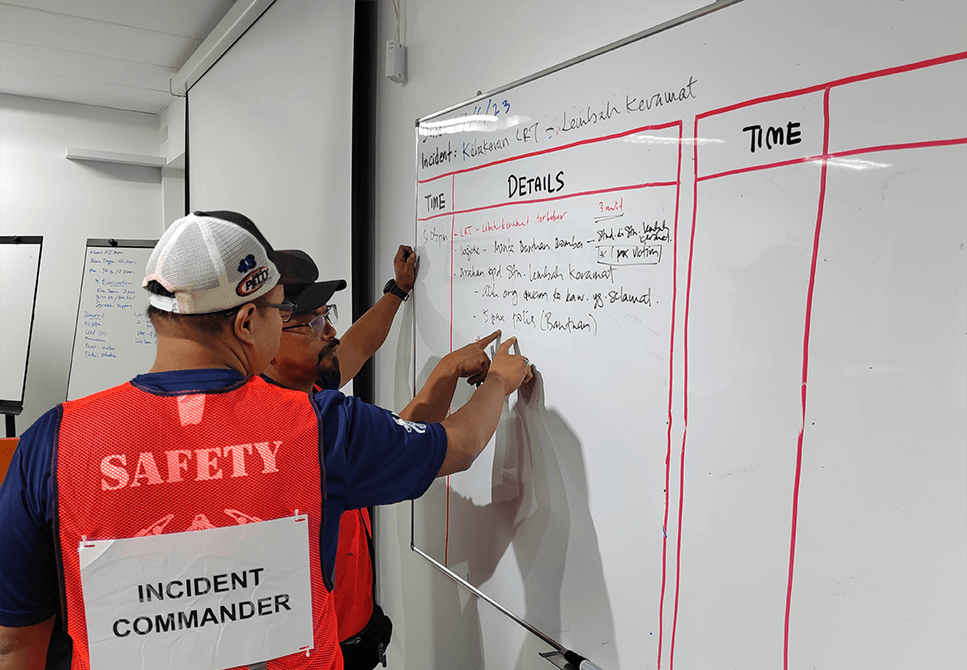
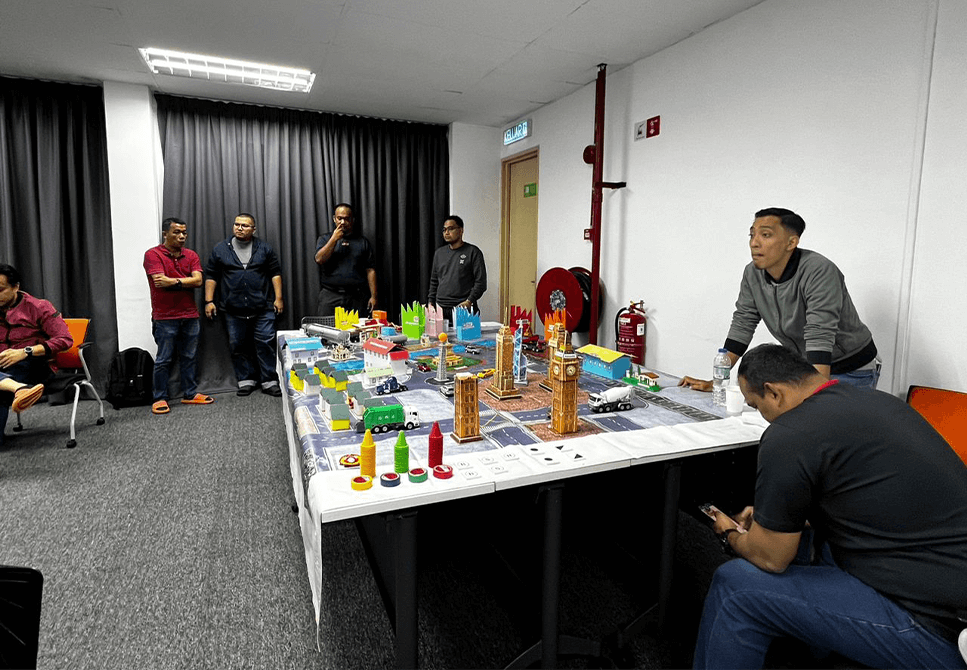



Professional Incident Commanders & Crisis Management Team trainers
Our training obtains an average of 4.9 stars out of 5 on Google Review.
Mr. Wong Wee Zhee
Master Trainer
Mr. Muhammad Muazzam Bin Jamaluddin
International Trainer
Mr. Muhammad Zabidi Bin Zoulkifli
International Trainer
Training modules of ICCMT Development Program
Let us know if you have specific requirements or needs.
| Components / Training courses | ICCMT Level 1 | ICCMT Level 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Response planning at workplace | Layers of response plan | ✔ | - |
| Response plan level and its implication | ✔ | - | |
| Escalating response plan | ✔ | - | |
| Roles of ERT & response plan | ERT organization | ✔ | - |
| ERT activation | ✔ | - | |
| Team formation | ✔ | - | |
| 7 critical tasks | ✔ | - | |
| Table top drill | ✔ | - | |
| Team strategy & tactical | Firefighting | ✔ | - |
| Hazmat Response | ✔ | - | |
| Incident Command System (ICS) | Introduction | ✔ | - |
| ICS management by objectives | ✔ | ✔ | |
| ICS organization & function (FEMA ICS 100) |
✔ | ✔ | |
| Setting up Emergency Operation Centre (EOC) (FEMA ICS 200) |
✔ | ✔ | |
| Planning P (FEMA ICS 300) |
- | ✔ | |
| Parallel Emergency Operation Center (EOC) | - | ✔ | |
| Execises & drills | ICS exercise | ✔ | ✔ |
| Table top exercise - 5 tables | ✔ | ✔ | |
| EOC command & control exercise | ✔ | ✔ | |
| ICS function drill | - | ✔ | |
| Planning P and operational period exercise | - | ✔ | |
| Parallel Emergency Operation Center (EOC) exercise | - | ✔ | |
| Major drill with parallel EOC and cross operational period | - | ✔ | |
Organizations that had trained their Incident Commander & Crisis Management Team
Emergency response can never be too ready.
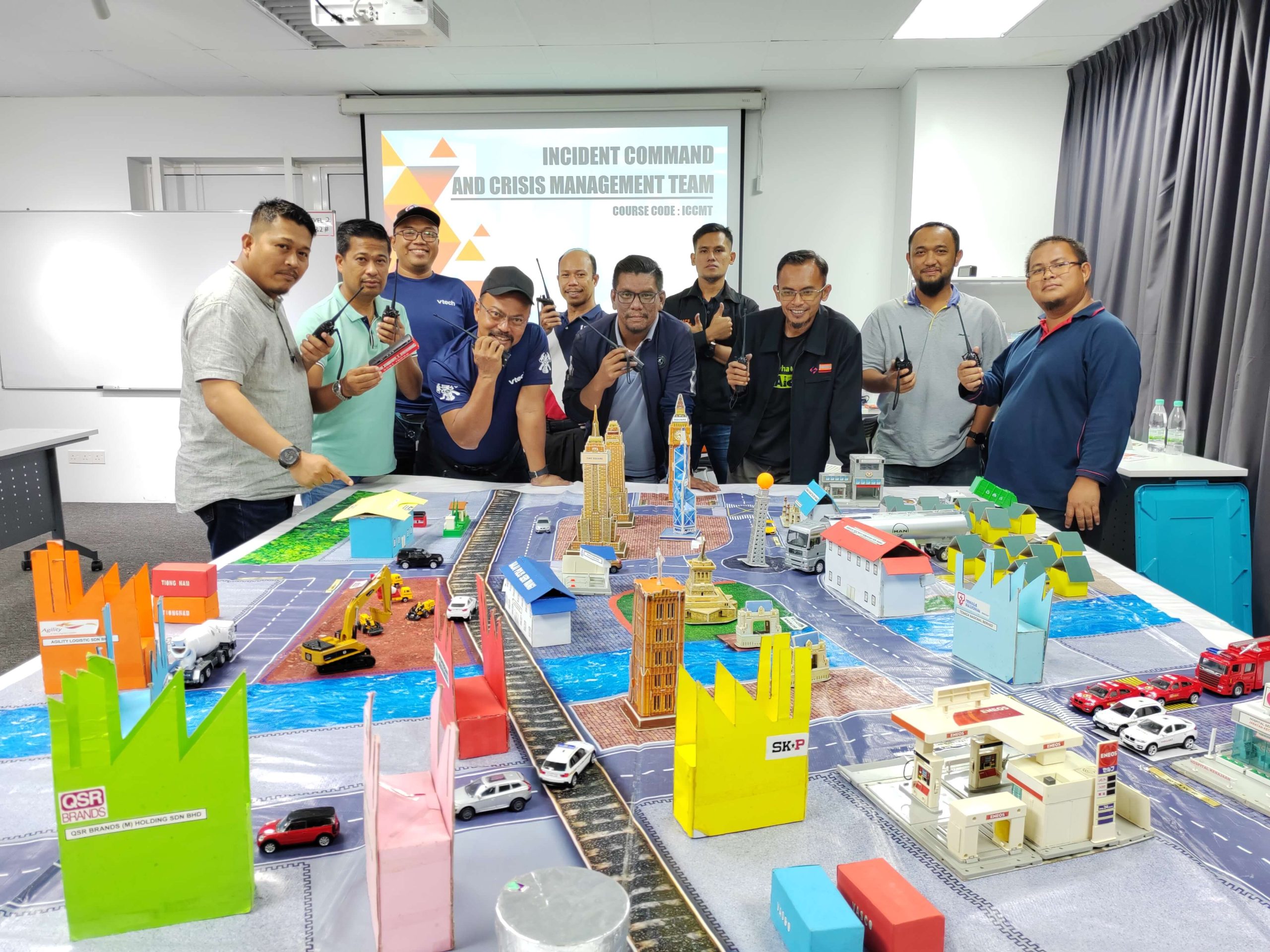














Establish your incident commander & crisis management team
For organizations that strive to be well prepared for an emergency response beyond the workplace.
